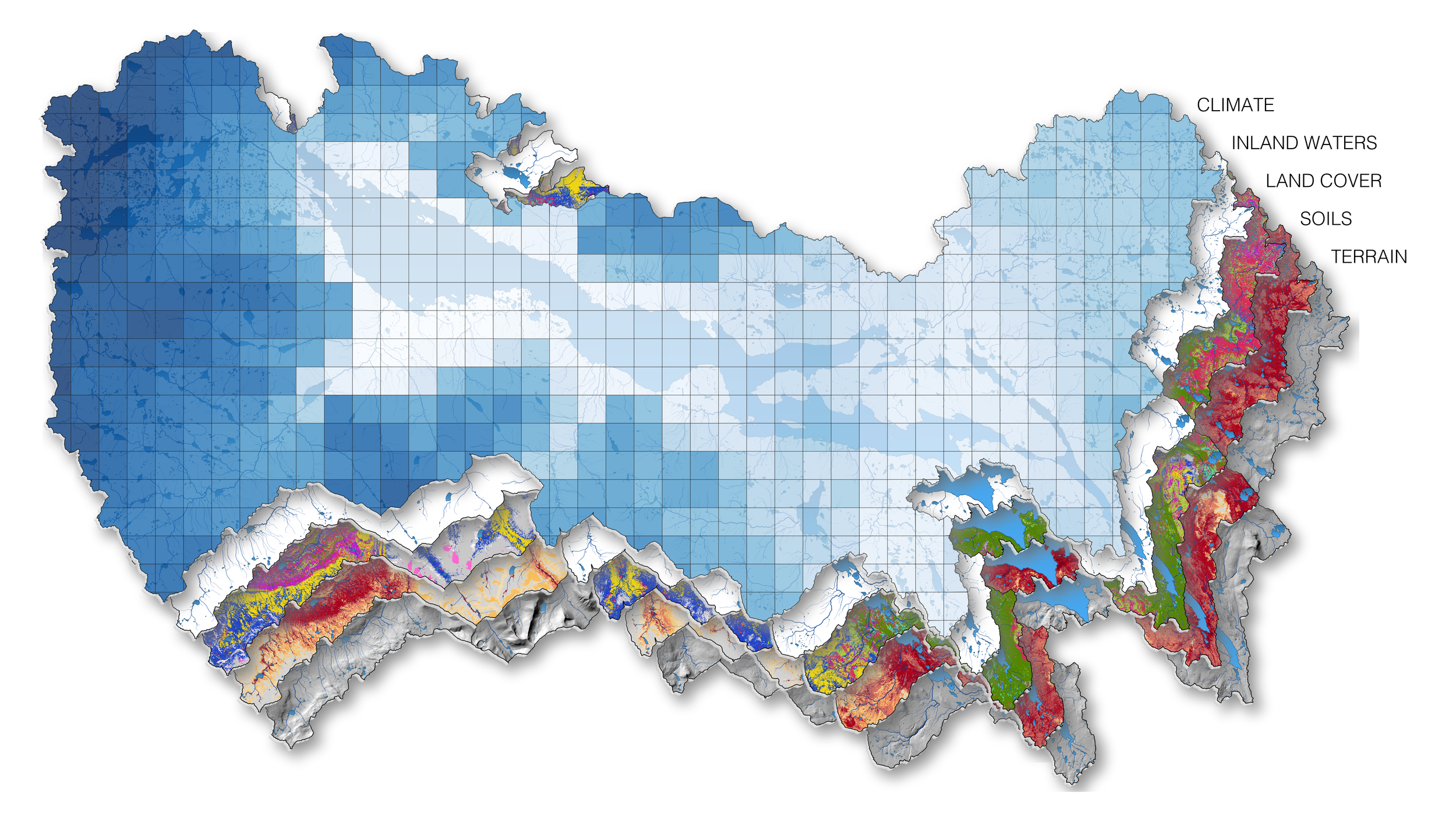
Abisko-HYPE
HYPE is a hydrological model developed by the Swedish Meteorological and Hydrological Institute (SMHI). HYPE and the current version of Arctic HYPE are widely used internationally and are effective at broader scales. However, in the Fennoscandian Arctic and smaller basins, they face limitations, lacking the detailed resolution necessary to fully capture the hydrological, biogeochemical, and ecological dynamics crucial for understanding climate change impacts. These models require further calibration and constraints to enhance their precision at smaller scales.
We aim to achieve the highest possible spatial and temporal resolution to advance climate research across the land-water continuum with an implementation tailored to the Torneträsk catchment in the Abisko region. To this end, CIRC established research agreement with SMHI to bolster this collaborative project. This collaboration signifies a pivotal step toward realizing a tailored hydrological model that will significantly contribute to our understanding of the interplay among climate drivers, terrestrial systems, and hydrological dynamics in the Abisko area, offering a framework to connect research carried out at CIRC over the long term. The implementation of the HYPE model offers multiple benefits for CIRC research, facilitating a multidisciplinary approach across various environmental studies. Below are a few examples how researcher with different research backgrounds within CIRC can leverage on the HYPE model outputs:
Anticipated improvements of the Abisko-HYPE model, resulting from the collaboration between SMHI and CIRC researchers, are expected to introduce an array of new functionalities. These enhancements, driven by the integration of unique data, will include, but are not limited to improved estimates on export of carbon and nutrients from land, better integration and coupling of lake physical dynamics and biogeochemical cycling within complete hydrological networks, and enhanced simulation of the sensitivity of carbon cycle components to climate change in an Arctic setting. These enhancements will further support CIRC's mission, fostering an integrated understanding of environmental dynamics and climate interaction.
For further information, please contact: Cristian Gudasz (CIRC), Andrea Popp (SMHI), David Gustafsson (SMHI)